Natural Language Processing (NLP), MLOps, SCRUM

We analyzed Expeditie Robinson (Survivor) to identify which content elements resonate with viewers. Using content classification (actors, actions, emotions) and speech-to-text, we automated labeling of Ekman’s six emotions—happiness, sadness, fear, anger, surprise, disgust—based on existing emotion-tagged data to enable more personalized viewing insights.
We used training, test, and application datasets. Training combined nine sources (e.g., Reddit, Twitter, Friends scripts, fairytales) plus the LIAR dataset (12.8K labeled statements) for linguistic diversity. For the main use case, Banijay Benelux supplied 17 videos; we extracted audio, transcribed, translated (NL→EN), and segmented by timestamps.
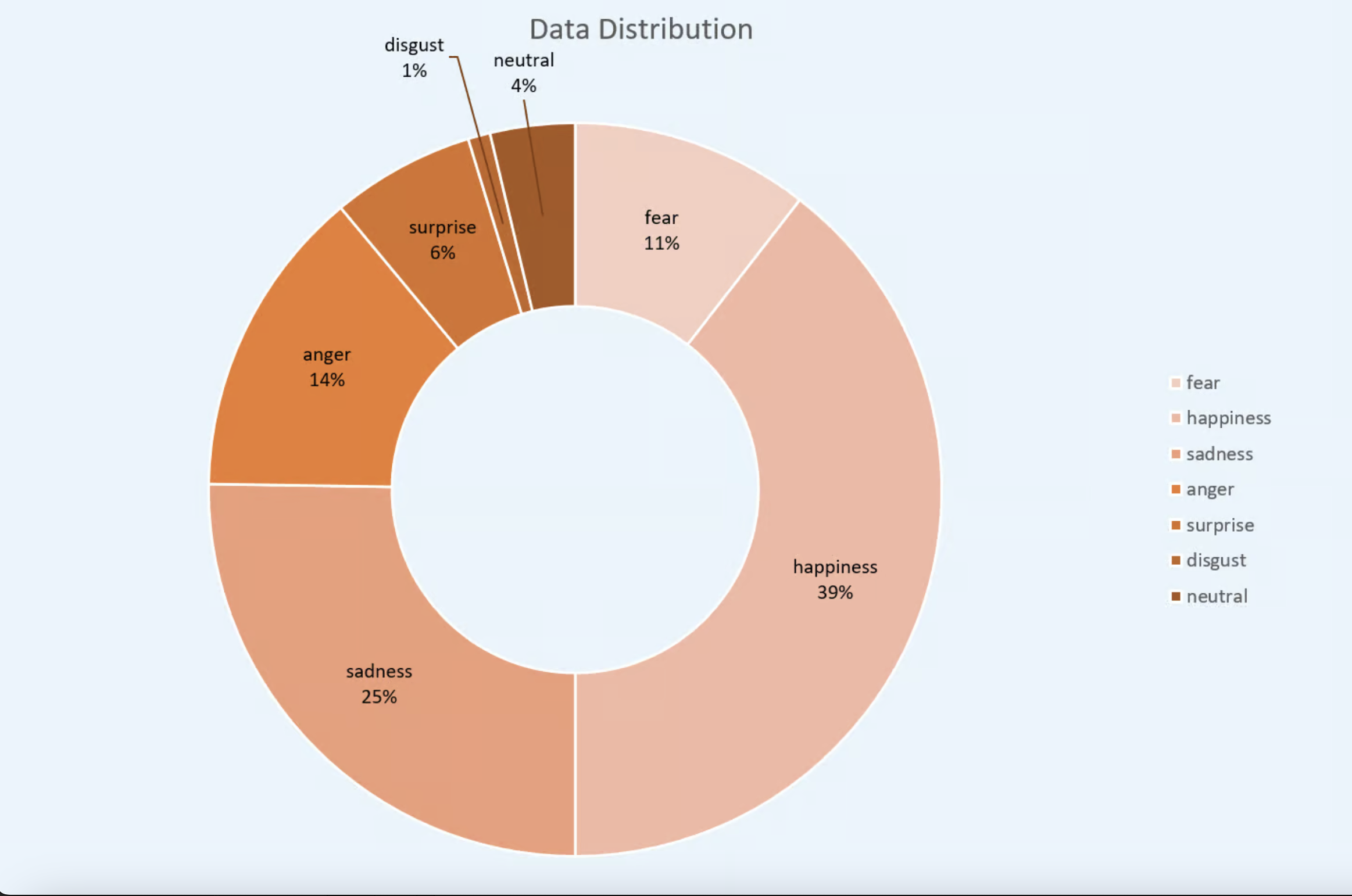
Happiness dominated (224,422 sentences) while disgust was scarce (5,550), revealing a strong class imbalance likely to hinder performance on rare emotions.
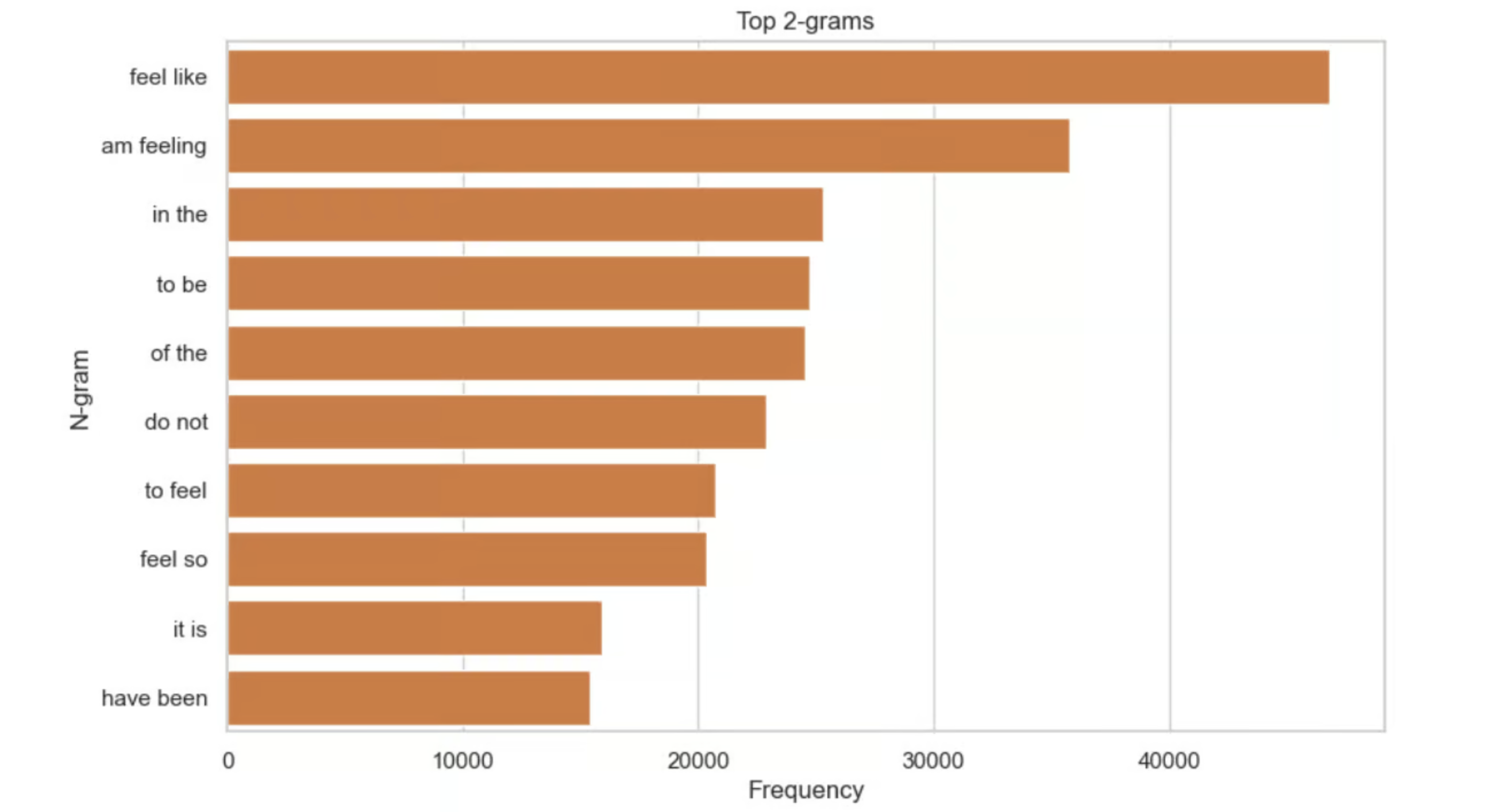
N-gram analysis (bigrams) captured syntactic/semantic cues. “feel like” was most frequent (46,816), with common collocations like “in the,” “to be,” and “of the,” informing contextual emotion cues.
A word cloud highlighted the most frequent terms, reinforcing n-gram findings and guiding feature understanding for emotion classification.
We compared statistical and neural models. After fine-tuning BERT, we switched to RoBERTa due to its training approach and stronger context modeling, which better captured nuanced emotional language. RoBERTa was selected for the final system.
We delivered an end-to-end pipeline to transcribe, translate, and emotion-tag video segments. It achieved accurate segment-level predictions and actionable engagement insights for Banijay Benelux. Key learnings: address class imbalance, maintain data quality, and prefer architectures (like RoBERTa) that excel at contextual nuance.